
Launching a new Google Ads search campaign is an exhilarating process. Excitement, anxiety, fear, and hope are emotions that come to mind when I’m about to click the Enable button on a new campaign.
If you are just getting started, you might be afraid of messing it up. I get it. The steps I’ll walk you through will ensure you’re depositing more money into your own bank account, rather than just funding Google’s empire.
When set up and managed properly, Google Ads (previously Google Adwords) is one of the best sources for new customers.
Over the years, I have helped businesses grow from $0 to $1,000,000+ on the back of hardworking AdWords campaigns. But, I’ve also watched tens of thousands of dollars get flushed down the AdWords drain due to mismanaged campaigns.
So let’s get down to it. Tie on your AdWords apron, grab a pen to write down the key steps of a successful Google Ads Campaign, and follow along as I walk you through how to create a profitable Google AdWords campaign from scratch.
Google Adwords Step #1: Is There Customer Demand?
If your customers are not searching for your product or service in Google, then obviously, AdWords search advertising is not going to work for you.
So, before you get too excited about creating your first campaign, you need to verify there is, in fact, search volume for what you’re going to offer.
I suggest using UberSuggest, which is my own free keyword research tool. The keyword tool acts much like a thesaurus. You enter in phrases you think your prospects are searching, and it will tell you other similar, relevant phrases.
Ubersuggest will tell you how often people search these phrases, how competitive the keywords, and how much it’ll cost to advertise on each keyword. All of this information will help you determine which keywords you want to use in your first campaign.
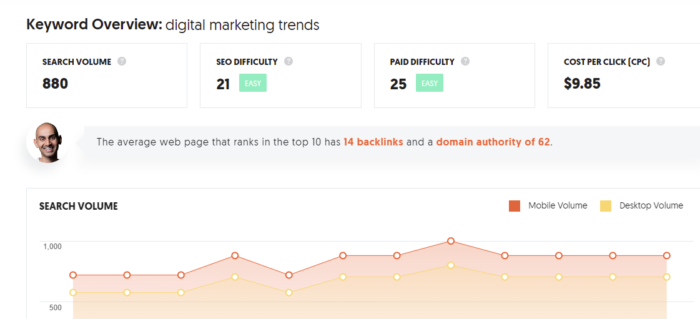
I also recommend you use the keyword “Suggestions” provided under the main chart. This will give you an idea of related keywords and how much search volume those keywords have.
You can also use Google’s Keyword Planner tool to help you find the best keywords to target. It will provide you with bid estimates and total searches, so you can make a plan.
There are three questions you’re going to ask to determine whether or not to advertise on a particular keyword:
- Is the keyword searched in Google? If there is no search volume, then that tells you no one is typing that phrase into Google. There is no point in advertising on keywords no one is searching.
- Is the person searching this keyword likely to buy my product or service? Or is the person more likely just doing research with no intention of making a purchase? In other words, what is the intent of the keyword? When starting out, you’ll want to advertise on what I call “buying intent” keywords where the person is clearly looking to buy.
- Can I afford to advertise on the keyword? This question is important, but it requires a bit of math to calculate. So let’s take a look at that now.
Google Adwords Step #2: Can You Afford to Advertise on Top Keywords?
Before finalizing your keyword list, you must make sure it makes sense to target that term. This will prevent you from going after keywords where there’s no chance of them being profitable. It’s better to run these numbers now before you’ve sunk time and money into a campaign destined to fail.
To answer the question “Can I afford to advertise on this keyword?” you need to calculate your maximum cost per click (Max CPC). You’ll compare your business’s Max CPC to the estimated keyword CPC in the Keyword Tool to see if you can afford to advertise.
For example, if your Max CPC is $5 and the estimated CPC is $4, then you know there’s a good chance you can profitably advertise on that particular keyword.
Your Max CPC is determined by your website’s conversion rate, profit per customer, and target advertising profit margin. If you don’t know these numbers, you’ll need to guesstimate or set up tracking to calculate them more accurately.
Use the formula below to calculate your Max CPC and then compare to the estimated CPC you found above:
Max CPC = (profit per customer) x (1 – profit margin) x (website conversion rate)
For example, let’s say your average profit per customer is $500, and out of 1,000 website visitors, you convert 10 into customers. That means you have a 1 percent website conversion rate.
If you are comfortable with a 30 percent profit margin, then here’s how you would calculate your Max CPC:
Max CPC = $500 x (1 – 0.30) x 1% = $3.50
Again, your Max CPC must be in the neighborhood of the estimated CPC in Google’s Keyword Planner tool, or else you’re in trouble.
Suppose your Max CPC is $3.50 and the estimated CPC for a keyword is $10. In that case, you’ll need to first increase either your profit per customer or your conversion rate before you can profitably advertise on that particular keyword.
Google Adwords Step #3: Perform Competitor Analysis
At this point, you now have a list of “buying intent” keywords that you’re confident you can afford. The next step is to reduce your risk by leveraging competitor intelligence.
In most industries, you’ll find competitors who already have tested and optimized their AdWords campaigns. That means they have figured out which keywords, ads, and landing pages work and do not work in your market.
Wouldn’t it be great if you could just hack into your competitor’s AdWords accounts and steal that information?
Before you get too far along on your illegal hacking plot, I should let you know about a very cool competitive intelligence tool called KeywordSpy. KeywordSpy collects, organizes, and provides easy access to all of your competitors’ historical advertising information.
Think of it like your own Delorean time machine!
To set up your account, go to www.KeywordSpy.com and click on the free trial button.
Once you’re signed up and logged in, then copy one of your competitor domains into the search bar and select the Domains option as shown below.
(To find your competitors, simply type your keywords into Google and then copy the advertiser domains.)
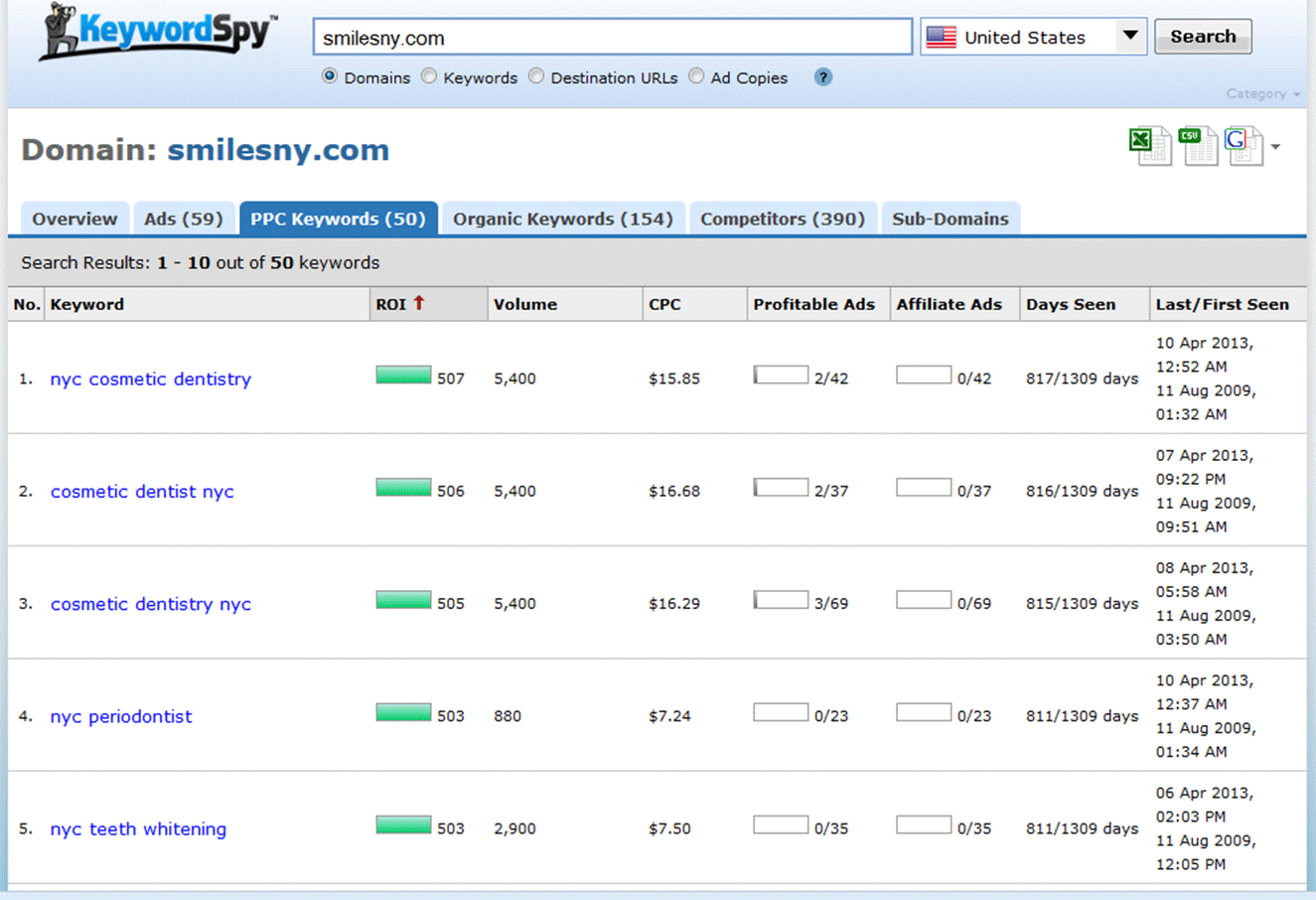
When the search is complete, click on the PPC Keywords tab to see all of the keywords your competitor is advertising on.
In this example, the competitor is advertising on 50 keywords and you can see the date when they first started to advertise on each keyword. The longer an advertiser has been advertising, the better because that implies the keyword is generating sales.
If the keyword was not profitable, then a smart advertiser would pause the keyword.
(Important Note: Not all advertisers are smart, so don’t blindly use this rule of thumb.)
Next, you can either manually search through the list, or you can export them all, remove irrelevant keywords, and then add them to the list of keywords you already found in Ubersuggest or Google’s Keyword Planner tool.
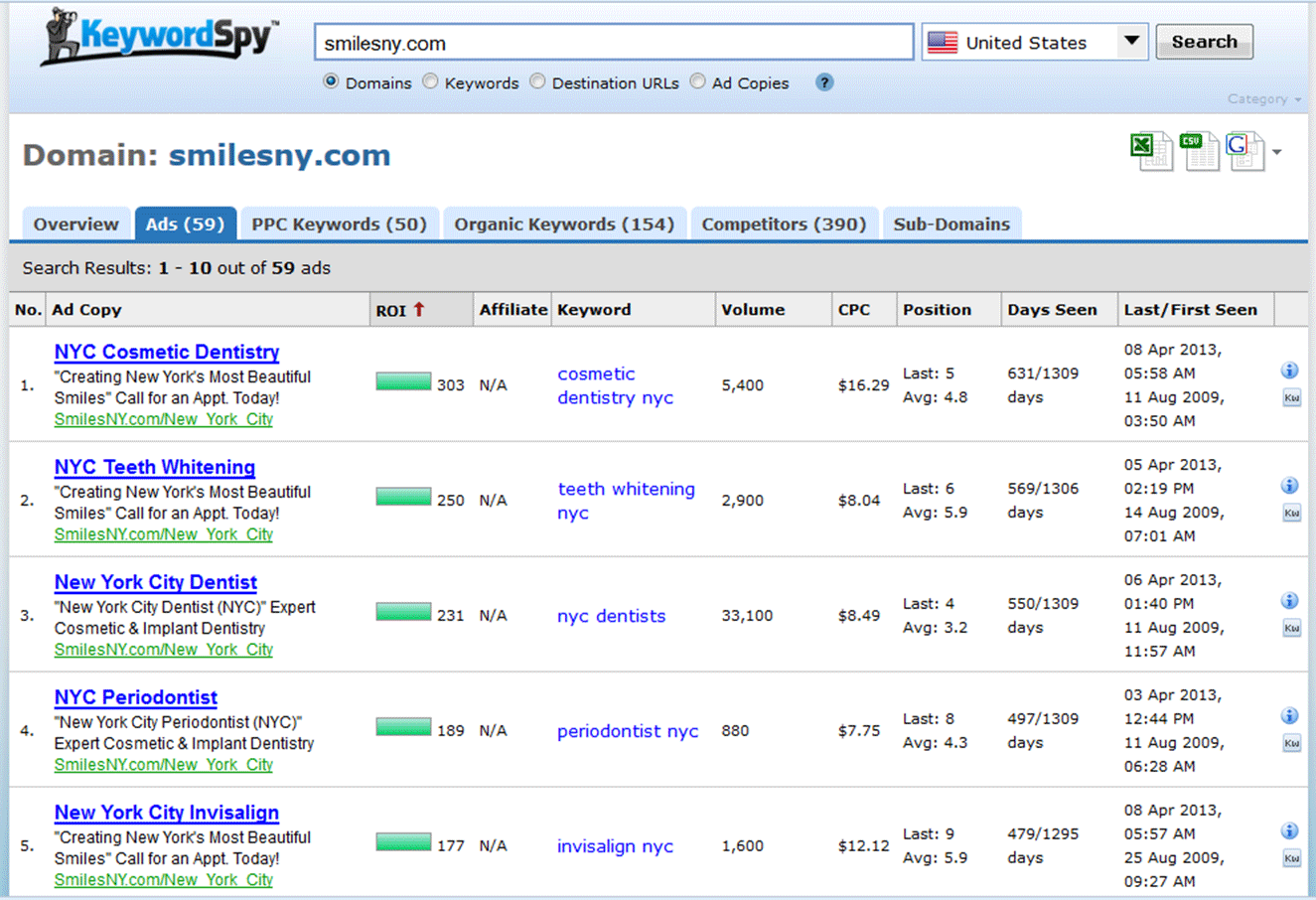
When you’re done reviewing keywords, click on the Ads tab to review your competitor’s ad copy.
Again, you can see the date when the ad was tested, which indicates whether or not the ad is performing well.
You can also use other competitive analysis tools to find out more about what works for your competitors.
I recommend reviewing several competitors’ ads to see what types of offers resonate with your target market. While you’re reviewing the ads, look for a way to differentiate your business from all of your competitors.
Differentiation is critical to AdWords’ success, which brings us to step four.
Google Adwords Step #4: Leverage a Powerful USP
Your USP, or unique selling proposition, is what differentiates your business from your competitors and gives your prospects a compelling reason to choose you.
In other words, your USP answers the question, “Why should I, your prospect, choose to do business with you, versus any and every other option, including doing nothing?”
When it comes to AdWords, there are three important reasons to create a powerful USP:
- A strong USP generates more traffic from qualified prospects (encourage clicks on your ads) and repels unwanted leads (prevent clicks on your ads).
- A strong USP will skyrocket your sales conversion rates. So, not only will you generate more traffic because you’ll get more clicks on your ads, you’ll also convert more of your traffic into paying customers.
- A strong USP can eliminate price comparison shopping. This can be a game-changer because you’re no longer seen as a commodity. If you give your prospects a compelling reason to do business with you versus your competition, then price becomes a secondary issue.
OK, a USP is a key ingredient. Makes sense, but how do you create one?
Well, first, you focus on your core strengths. What are you better at than your competitors?
Second, talk to your customers, and more importantly, listen to them. A great USP is built on customer insight, so ask your customers why they do business with you. Also, ask questions to determine what your customers dislike about your industry and what your customers wish you could provide in addition to your core products or services.
Third, analyze your competitors, and look for an opening. The most important word in unique selling proposition is unique.
To create a really strong USP, you need to study your competitors’ ads, websites, and marketing materials, and find your opportunity to stand out. I recommend you use a spreadsheet to organize all of your competitors’ ads and websites, so you can more easily find the commonalities. As you’re doing this, look for an opening to say something unique and superior.
To get you started, here’s a powerful USP I’m sure you’ll recognize: “Fresh hot pizza delivered in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed.”
Where have you heard that line before? That’s Domino’s Pizza’s USP, and they used it to build a billion-dollar empire.
They don’t claim to be all things to everybody. In fact, they don’t even mention quality ingredients, price, or taste. They focused their entire business on the one thing their customers care about most – fast, on-time delivery.
Picture some college students late Saturday night with the munchies, and you’re looking at Domino’s Pizza’s ideal customer profile!
Google Adwords Step #5: Have an Irresistible Offer
What can you offer in your AdWords campaign that is so compelling your prospect would be a fool to not take action? How can you stand out from all the other ads your prospect will see in the search results?
The answer is your irresistible offer, which consists of the following four components:
1. Valuable
Your product or service must be more valuable than the price. That’s marketing 101. This doesn’t mean your offer has to be cheap. You just need to clearly define all of the value your product or service provides to your customer and make sure it outweighs your price tag.
2. Believable
When you make an offer that appears to be too good to be true, then your prospect may be a little skeptical. So you must provide a believable reason for your offer.
For example, if you’re running a special sale, you need to explain why you’re offering such a steep discount. The reason could be anything: clearing out inventory, end-of-the-year sale, celebrating an anniversary, opening a new store, your birthday, and so on.
3. Reduce or Reverse Risk
Everyone is scared of getting ripped off online. One of the best tactics to minimize the risk to your customer is with a money-back guarantee. A money-back guarantee puts all the risk on your business to deliver excellent service, or else you’ll have to give all the money back to the customer.
Whenever possible, I always recommend you include some kind of guarantee in your offer. It will improve your response rates, and it’s a great way to differentiate yourself from your competitors.
4. Call to Action
One of my elementary school art teachers once gave me fantastic advice when he was teaching a class. He told me to always “Use the KISS method… Keep it simple, stupid.” I didn’t realize at the time, but those truly are words to live by, especially when you’re creating an irresistible offer.
If you want your prospect to pick up the phone and call you, then make it crystal clear and simple to call you. Don’t expect your prospect to connect the dots or search around your website to figure out the next step. Use a strong call to action and keep it simple.
At this point, you’re probably wondering if you’ll ever actually create your AdWords campaign. We’re already halfway through the steps, and you don’t have any ads to show for it!
Trust me, the first five steps are absolutely critical, and you’ll thank me later once you’re ads are live and you’re generating profit, instead of loss.
But since you asked for it, let’s dive in and talk about creating your ads.
Google Adwords Step #6: Create Compelling Ads
With AdWords search advertising, you pay only when people click on your ads. Therefore, your ads have two very important jobs:
- Attract qualified prospects so they click on your ad instead of competitors’ ads.
- Repel unqualified prospects so they do not click and waste your ad budget.
That means more traffic, more sales, and less wasted money on unqualified traffic, which all leads to higher profits for you.
There’s one more important job for your ads. Compelling ads with a high click-through rate (CTR) will boost your Quality Score, which in turn will lower the cost per click of your keywords.
So your ads will directly affect how much you pay per click for each of your keywords. Great ads will lower your costs, while lousy ads will raise your costs.
Do you see why step #6 is so important? This is also why all of the previous steps are required, because we’ll use them all to make the ads more compelling.
There are four key components to your AdWords text ads:
- Headline
- Description line 1
- Description line 2
- Display URL
Headline
The headline is the most critical component because it’s the first thing your prospect will read. Try to include your keyword in your ads’ headline because Google will bold the text, which makes it stand out from other ads.
This also is the easiest way to ensure your ad is 100 percent relevant for the prospect searching.
Another great strategy is to ask a question in the headline. For example, if the keyword is “new york city dentist” then a compelling headline is “Need a New York Dentist?”
Not only is part of the keyword in the headline, but the question will get the prospect nodding her head yes. As all great salespeople know, just one yes is sometimes all it takes to start a chain reaction leading to the sale.
Google AdWords allows 30 characters for your headline so make every letter count and use abbreviations whenever possible.
Description Line 1 and 2
In your two description lines, reiterate the benefits of your service, state your USP, provide social proof, and/or describe your offer. And, of course, include your call to action. You only have 35 characters for each description line so, again, use abbreviations to fit more of your message.
Display URL
The display URL is an easily overlooked area of your ads. Don’t just copy and paste your domain name. Instead use your Display URL to include your offer, your call to action, your USP, or anything else that will make your ads stand out.
Here are three examples for a dentist to give you an idea of what you can do:
- https://ift.tt/2Rs2zze
- https://ift.tt/32iE8q0
- https://ift.tt/32eMLSB
Before we move on, I want to show you an example of a good ad and a bad ad, so you can see the difference.
Example of a Good Ad for the Keyword “appliance repair”:
Same Day Sub-Zero Repair
24 Hour Service… Within 1 Hour
$25 Off Coupon. Call Us Now.
As you can see, the advertiser is clearly targeting a specific niche – people with Sub Zero appliances. They offer compelling benefits, including same-day 24-hour service within one hour. They have an offer of a $25-off coupon. And they have a clear call to action to call now.
Note that I would try to improve this ad by including the keyword in the title to make it more relevant to the search phrase.
Example of a Weak Ad for the Keyword “appliance repair”:
[Name of Company]
family owned since 1939 for all
your appliance needs call now
The headline of this ad was the name of the company, which is not relevant to the keyword “appliance repair.” Unless you’re a big-name brand, no one will recognize or even care about your name. It’s not compelling and there’s no congruence from keyword to the ad.
Also, “family owned since 1939” is not a specific benefit. There’s implied benefit if the prospect puts two and two together and believes longevity equals good service. However, that’s a lot to ask and clearly does not follow the KISS principle. Stick to explicit benefits rather than implied benefits in your ads.
Finally, the phrase “for all your appliance needs” is as vague as you could possibly be. This is an example of trying to be all things to all people, rather than solving a very specific problem for a very specific target customer.
Google Adwords Step #7: Use Relevant Landing Pages
At this point, your prospect has searched for your product or service. They found your ad to be compelling versus all of the other options, clicked to learn more, and landed on your website.
Now what?
Well, if you’re like a lot of first-time advertisers, then your prospect is now on your homepage scratching their head trying to figure out what just happened. The ad made a promise the homepage couldn’t keep.
That’s because your homepage is not an advertising landing page!
Homepages explain everything your business does, all of your products and services, and all of the different customers you serve. In other words, your homepage is not 100 percent relevant to the keyword searched and the ad clicked. Do not make this mistake.
Instead, create a dedicated landing page that matches the keyword and the ad. The goal is to make the entire sales process congruent so your prospect is continually reassured she’s going down the right path.
The most important component on your landing page is your headline, which is the first thing your prospect will read. Your headline must grab attention, reiterate the offer made in the ad, and compel your prospect to keep reading the rest of the page.
The copy of high-converting landing pages should again be relevant to the keyword searched and the ad clicked on. Include your USP, benefits of your product or service, details about your irresistible offer, social proof, credibility that you’re a legitimate business, and a strong call to action.
Google AdWords Step #8: Conversion Tracking
We’re almost ready to set up your campaign in AdWords, but there is one final ingredient: Conversion tracking.
If you skip this step, you’ll never know which keywords and ads generate sales and which are just losing money. In other words, you will not be able to optimize your campaign once it’s up and running.
Conversion tracking measures the sales generated by your AdWords campaign. More specifically, you want to know which keywords and which ads are generating sales.
If some or all of your sales occur online with an e-commerce shopping cart, then conversion tracking is pretty straightforward. Just use the built-in Google AdWords conversion tracking.
The Google Ads conversion tracking code can be found in your Google Ads account under the tool icon, then “Measurements > Conversions.”
To create a new conversion, simply click on the [+ Conversion] button and follow the steps to define your conversion. Then add the small snippet of code to your order form thank-you page or receipt page.
This code is similar to Google Analytics code if you have that installed on your website, but it should be on only the final page after a customer completes her order.
Then, when a customer lands on your receipt page or thank you page, Google will track the conversions in your AdWords account automatically. That’s really all there is to it, and there’s no reason not to install this before you turn on your ads.
Google can also track app installs, web conversions, phone calls, and offline conversions.
What if you generate leads online, but you ultimately close the sale “offline” – over the phone or in-person – rather than online? Clearly, you can’t add a conversion code to your cash register, so what can you do?
The three tactics I recommend for tracking offline sales are:
- Create a conversion page in your sales process. For example, send all of your customers to a special page to get their receipt, create an account online, or download an important document. Think of a way to get your customers to that webpage and add the AdWords code to that page. Now you can track the sales.
- Use unique coupon codes in your ads and landing pages. If you use unique coupon codes in your ads and landing pages, then you can match the codes back to the ad and keyword that generated the sale.
- Use tracking phone numbers in your ads and landing pages. If you use unique tracking phone numbers, you can match the calls and subsequent sales to the ads and keywords that generated the sale.
Once conversion tracking is in place, then the time has finally come to log into Google AdWords and set up your first campaign.
The Google AdWords interface makes campaign setup a breeze, but don’t blindly accept the default settings. Some of them can get you into trouble.
Google AdWords Step #9: AdWords Settings for Success
As I mentioned, Google Ads does a great job of making it fairly easy to set up your campaign. Simply click on the blue plus symbol, then the New Campaign button, as shown below, and follow the steps to add in your ads and keywords.
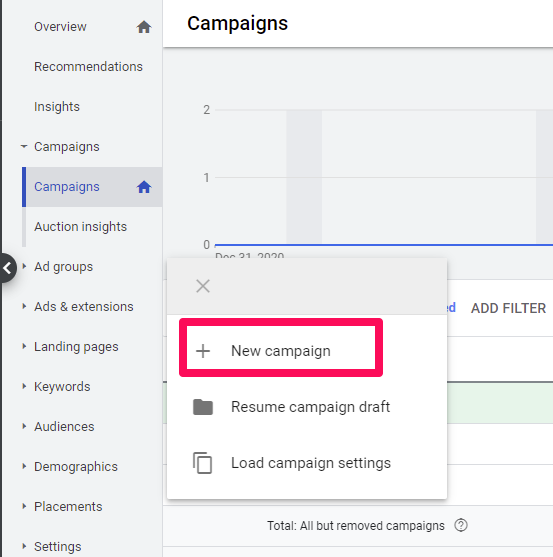
The process is pretty simple; however, many of the default settings are not in your best interest. That’s why step #9 is to use the correct AdWords settings for success.
Here are the most important settings to watch out for:
- Search vs. Display
- Device Bids
- Keyword Match Types
- Negative Keywords
Search vs. Display
Select Search Network Only for your campaign type, so you’re targeting only the Google Search Network and not the Display Network.
The display network is a completely different animal than search advertising and it requires a different set of keywords, ads, and landing pages. So always set up separate campaigns to target each network.
Keyword Match Types
Many first time advertisers have no idea there are different match types. As a result, they waste money on irrelevant search phrases that are not part of the keywords listed in the account.
There are three main keyword match types:
- broad
- phrase
- exact
Broad match as you now know is the default match type. If you leave your keywords as Broad match, then Google will show your ads to any search phrase Google thinks is relevant to your keyword.
This means your ads will get more impressions, but you’ll likely show ads to irrelevant search phrases that will just waste your budget. So I do not recommend Broad match.
Phrase match keywords will trigger ads when the exact phrase is part of the keyword typed into Google. For example, if your Phrase match keyword is “office space,” then your ad will display for “New York office space” and “office space in New York.” However, your ad would not display for “office in space” because the phrase “office space” is broken up by the word “in.”
Phrase match gives you much more control over your ads than Broad match. To change your keyword to Phrase match, simply add quotes around the keyword (see image below).
Exact match simply tells Google to display your ad only when the exact keyword is typed into Google. You’ll get the most control with Exact match, but you’ll limit your exposure. To set your match type to Exact match, add square brackets around your keywords (see image below).
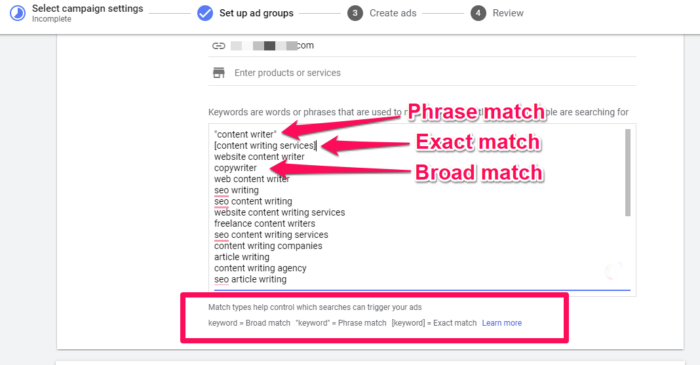
I recommend starting with Phrase match because you’ll get the best of both worlds with regard to targeting and reach. However, when you use Phrase match, you need to make sure you include negative keywords.
Negative Keywords
Negative keywords give you the ability to block phrases from triggering your ads. For example, if you’re an office space rental company advertising on the Phrase match keyword, “office space,” then you will want to block the keyword “movie.”
That way your ads for an office space rental will not be displayed for folks searching for the Office Space movie.
To add negative keywords, go to the Keywords tab in your account, scroll down, and click on the Negative keyword link (see image below).
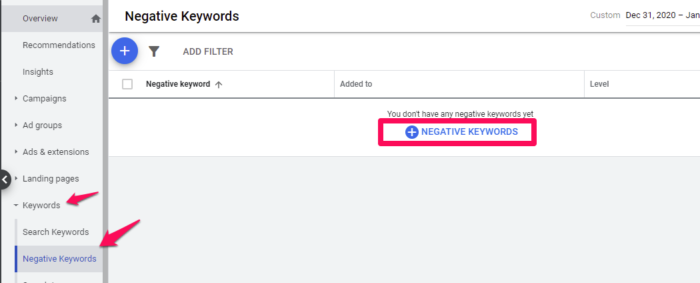
Next, click the Add button to add in the keywords you want to block.
Once you’ve completed the setup process, then you’re ready to enable the ads and start optimizing your campaign!
Google Adwords Step #10: Optimization
As soon as you set your bidding, enable your campaign, and Google approves your ads, you can take a nice deep breath. Congratulations, your ads are live!
Unfortunately, you can’t relax yet. Most campaigns are not profitable from the start and they always require continual optimization to stay profitable.
There are three main areas to improve your AdWords campaign performance:
- Your keyword bids. I recommend using Smart Bidding to get started, but once you start to generate clicks and sales, you might want to adjust your bids accordingly. If your keywords are generating sales profitably and you’re not ranked #1, then continue to raise your bids. If your keywords are not generating sales profitably, then obviously, you’ll need to lower your bids or pause the keyword entirely.
- Your ad click-through rate (CTR). As I mentioned earlier, your ad CTR directly affects your quality score, which in turn determines how much you pay per click. To optimize your CTR, A/B test different ads to see which version gets the most clicks.
- Your landing page conversion rate. The final area to optimize is your landing page. There are many tools to help you test different landing page versions, but if you’re just starting out, I recommend you use Google Optimize. It’s easy and free to get started. Create an experiment to test two different versions of your landing page and measure to see which one generates the most conversions.
Conclusion
By now, your Google AdWords campaign should be set up so you’re focused on optimizing keyword bids, ad click-through rates, and landing page conversion rates.
If you follow these ten steps, then you will be well on your way to a profitable Google AdWords campaign. Good luck!
Have you launched a successful Google Ads campaign? What tips do you have to share?
The 10-Step Guide to Creating a Profitable Google AdWords Campaign from Scratch
Publicado Primeiro em Neil Patel
Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário